Students from 3 engineering colleges have innovative ideas
Students from 3 engineering colleges have innovative ideas
Mangalore Today News Network
Magalore , June 19, 2014: Hybrid Bike, developed by final year mechanical engineering students of Karavali Institute of Technology. Two-wheeler users save fuel and money with a more powerful ride.
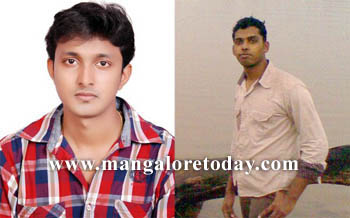 Two, Karavali Institute of Technology’s final year B.E Mechanical students Subin Daniel Thampi and Anaju Issac have developed the ‘TwoWheel drive bike,’ which runs on both petrol and electrics, by batteries and motor, as part of their final-year project work. While the regular two-wheeler has only back wheel drive, Hybrid Bike has both front wheel and back wheel drives. This was achieved by attaching a separate battery powered hub motor to the front wheel. This is said to be a new technology in the automotive industry. By activating this two wheel drive system, the biker can attain more power than ordinary bikes. Hero Honda CD-100 gear was modified into Hybrid Bike by attaching a 550W hub motor to the front wheel. it is stated that on the battery mode alone it will have a speed of around 60 kmph.
Two, Karavali Institute of Technology’s final year B.E Mechanical students Subin Daniel Thampi and Anaju Issac have developed the ‘TwoWheel drive bike,’ which runs on both petrol and electrics, by batteries and motor, as part of their final-year project work. While the regular two-wheeler has only back wheel drive, Hybrid Bike has both front wheel and back wheel drives. This was achieved by attaching a separate battery powered hub motor to the front wheel. This is said to be a new technology in the automotive industry. By activating this two wheel drive system, the biker can attain more power than ordinary bikes. Hero Honda CD-100 gear was modified into Hybrid Bike by attaching a 550W hub motor to the front wheel. it is stated that on the battery mode alone it will have a speed of around 60 kmph.
The fully charged battery can run for 6.5 hours, using three units of power at a cost of just Rs 10, making it highly economical. The students developed the project under the guidance of Prof P Ramesh Kumar of the College.
Disposing PVC waste
The final year civil engineering students of Shri Madhwa Vadiraja Institute of Technology and Management, Bantakal, have developed a novel way for disposing off the PVC dust available as a waste material in PVC product manufacturing industries. The dust is otherwise dumped with waste materials, creating health hazards.
The primary objective of the project was to develop construction material like concrete, by incorporating the industrial waste materials like PVC dust and, to convert it as an environmental friendly and cost effective construction material. Laboratory investigations were also carried out to compare the strength parameters of PVC dust concrete. The cost benefits were also analysed and found to be economical, which would have its impact in preserving the natural resources and also the environment. This project work was taken up as a part of their final year academic project and the team comprised of Rahul V Kotian, Prasanna N Bhat and Shashank G Hegde. The project was financially supported by Karnataka State Council for Science and Technology, Bangalore.
The students developed the project under the guidance of Assistant Professor at the Department of Civil Engineering, Anand V R and was supported by College Principal Prof Radhakrishna S Aithal, Dean (Academics) Prof Dr A Ganesha, and Civil Engineering Department Head Prof B Radheshyam, according to a press release from this college group.
Labour effective - Log splitting machine
With view to reduce tiring labour intensive process of manual log splitting motivated Rafath Abdul Razak, Sachin Kumar, Sankesh and Vachan Rao, final year students of Mechanical Engineering at Srinivas Institute of Technology to develop a machine to carry out the process. Using this machine, one can split logs continously in a much easier way. Logs available for firewood are generally three feet long and about six inch in diameter. Splitting is conventionally done using axe or saws is a laborious process . Shortage of manual labour has added to the problem. Even though there are saw mills or chain saws for cutting logs, such saw cut logs are not fit for burning since they do not ignite easily.
In order to solve the problem, this machine has been developed that splits wood in a similar manner as that of an axe but in an innovative way. It has a conical screw which is driven by an electric motor through a belt drive. Initially the log needs to be fed against the rotating conical tool for a short duration. Once the tip of the screw enters the log, due to the thread, the tool draws the log towards it. As the tool passes through, the increasing diameter splits the log into two. If the log gets jammed, a reversible switch is provided to reverse the tool rotation to expel the log out. Slightly longer firewood can be split by feeding at multiple points.
The project has been carried out under the guidance of Department of Mechanical Engineering Prof Sadashiv Lalasangi and Department Head Prof Thomas Pinto, stated a release from this college.
- No dossiers, only dose to terrorists: PM Modi’s poll blitz in Gujarat, Maharashtra
- Playback singer Uma Ramanan dies in Chennai
- Amid sex harassment charge, BJP’s Brij Bhushan, may be chosen in Polls
- Google lays off 200 ’core’ team employees, to shift jobs to India, Mexico: Report
- PM Modi’s 3rd term will eliminate terrorism from country: Amit Shah
- Heatwave red alert in six Karnataka districts as temperatures may cross 46 degrees Celsius
- Hindu marriage not valid unless performed with requisite ceremonies: SC
- GST revenues hit record ₹ 2.10 Lakh Crore in April. Here’s what led to it
- Deve Gowda planned escape of his grandson Prajwal, says Siddaramaiah
- Prajwal Revanna’s first reaction on sex tapes scandal: ’Truth will prevail soon’
- Accused in Salman Khan firing case dies after suicide attempt in police custody
- Indian space start-up uses spy satellite tech to track mosquitos
- Mangalore University hostel students protest against poor quality food
- Bonda factory gets clean chit in alleged food poisoning case
- Businessman succumbs to cardiac arrest while travelling in bus
- 123 couples tie the knot at mass marriage in Dharmasthala
- Mangaluru: CCB arrests two, seizes MDMA worth Rs 9 lakh
- Mangaluru :On May Day, TTEs stage protest at Central Railway station.
- Uppinangady: Woman missing with one year old daughter
- WhatsApp will soon block you from chatting temporarily if users violate its rules: All details
- Nasir murder case: Court sentences four convicts to life imprisonment
- Belthangady: Web cam stolen from polling booth at Thekkar
- Malpe: Life guards rescue 12 year boy from Chikkaballapura from drowning
- Man dies in freak mishap while tree felling
- Changes in train service
- New residential complex for the judges inaugurated in Mangaluru
- Absconding accused nabbed after 8 years
- Truck with cylinders turns turtle in Beltangady
- Bhoota Kola artist dies of cardiac arrest
- Development of the country should be our goal: Ganesh Karnik
- Container truck gets stuck under Modankap railway bridge
- Truck crushes bike’s pillion rider near BC Road
- Head constable dies of heart attack
- Udupi: PDO dismissed over financial irregularities
- CREDAI to resume Skill Development Program for Construction Workers in Mangaluru
- John B Monteiro elected president of Rachana Catholic Chamber of Commerce & Industry
- Sudhanshu Rai elected district president of All College Student Association
- Chief Minister to visit Mangaluru, Udupi on August 1
- Nitte University awards PhD degree to Tina Sheetal D’Souza
- Sachitha Nandagopal honoured by CMTAI for Community Service
- CITY INFORMATION
- TRAVEL
- TOURIST INFORMATION
- HEALTH CARE
- MISCELLANEOUS




 Write Comment
Write Comment E-Mail
E-Mail Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter  Print
Print 

